Maxilys®
Bioactive phospholipids to improve fat digestion
Maxilys® - Better nutrient digestion
Enhanced digestibility and advanced nutrient absorption
Getting the maximum from today’s high-density diets is key to optimize performance
Meeting the nutritional needs of intensive animal production is a challenge.
The use of supplemental fats and oils in animal diets as an energy source in intensive production is common practice. However, the high energy provided in modern, high performance diets is not in balance with the physiological excretion of bile salts and lipase in the animal intestine at each growth stage, with several consequences.
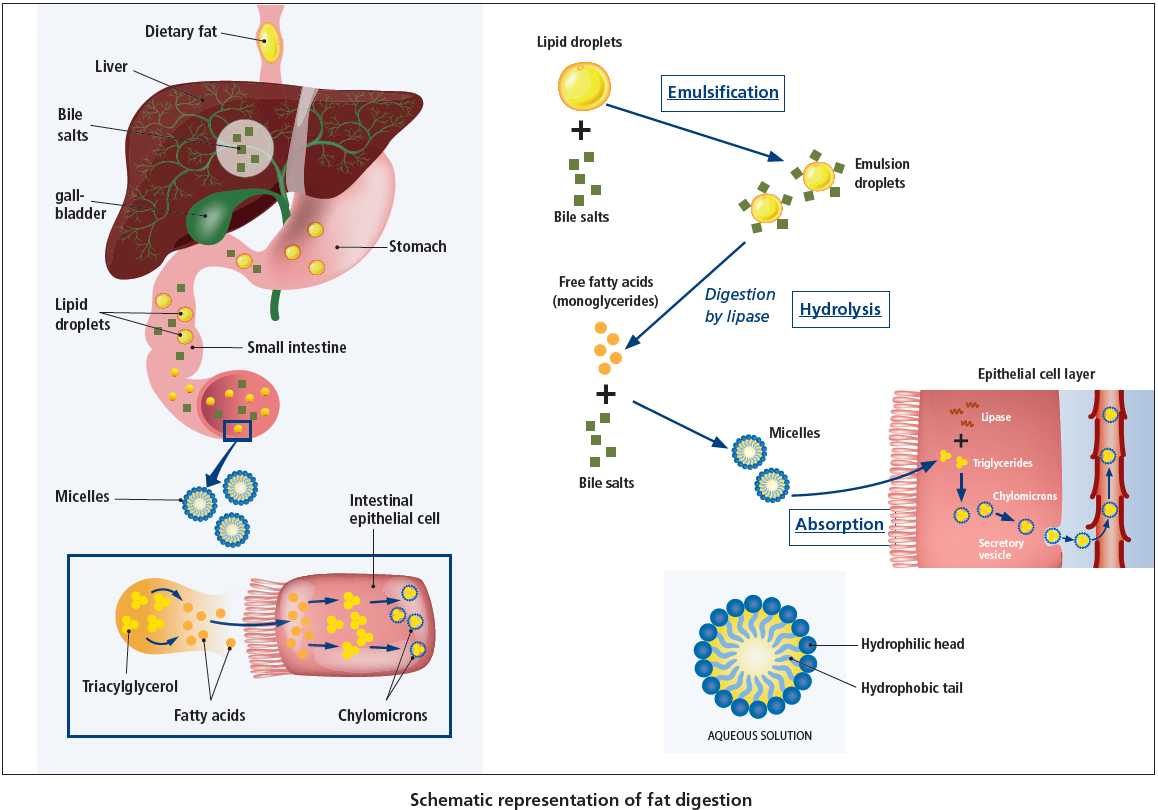
The natural process of fat digestion
Fats added to the diet enter the gastro-intestinal tract as part of the digesta in large coagulated particles. Bile salts excreted from the gall bladder enable initially the emulsification of these fat particles into smaller molecules in order to facilitate absorption by the intestine.
Decreasing the size of the fat globules results in the increase of the available surface area for the downstream action of the lipolytic enzyme, lipase. The role of lipases is to enzymatically digest lipid molecules (triglycerides) into a monoglyceride and two free fatty acids. However, inherently, fatty acids generated from lipase hydrolysis are water-insoluble, making their transportation through the unstirred water layer overlying the surface of the intestine impossible. Absorption of these molecules is facilitated by the formation of micelles – a process naturally mediated by amphipathic molecules such as bile salts and phospholipids
Maxilys®
Provides an optimal combination of enzymatically bioactive emulsifiers, designed for enhanced digestibility and advanced nutrient absorption by the animal.
Maxilys® supplementation can significantly improve breakdown and digestion of nutrients due to its bioactive content, by improving nutrient absorption provided from feed.
Maxilys® releases ‘feed-related stress’ from intensively reared animals and increases profitability.
The role of lysophospholipids
Phospholipids are biosurfactants naturally known to enhance the absorption of oils, fats and fat-soluble vitamins within diet. However, enzymatic hydrolysis of phospholipids results in the formation of lysophospholipids, which exert enhanced bioactive surfactant and nutrient absorption properties than their parent phospholipids.
Lysophospholipids exert superior emulsification properties by:
- Reducing interfacial tension and improved oil-in-water emulsions.
- Forming nutrient-dense aggregates, known as micelles, faster due to a higher critical micelle concentration (CMC) compared to their parent phospholipids. The higher the CMC the better the emulsification and subsequently absorption of nutrients.
- Forming smaller micelles in the small intestine thus, providing higher surface area for lipase activity
Lysophospholipids enhance the absorption of nutrients by:
- Improving digestion of fats
- Altering the physiology of cell membranes
These mechanisms result in increased passive and active transport of nutrients across the enterocytes and thus, increased nutrient digestibility, metabolic energy and animal growth.
Benefits
- Improved digestion and absorption of nutrients
- Weight gain and improved Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR)
- Improved growth during all stages of animal development
- Reduced inflammation and stress
- Support of liver and general health
- Profitability
- Improved pellet durability and quality
In-vitro testing
In this video, Innovad Group presents an oil in water emulsion capacity test. This in-vitro test shows that Maxilys® bioemulsifier performs significantly better compared to emulsifier categories most commonly used by the animal nutrition industry.
In vivo-tests have demostrated that Maxilys® consistently improves zootechnical performances and nutrient utilization in the main monogastrics and aquatic animal species.
Product composition and positioning may vary by market based on the regulatory status.
